Covalent Bond Ceramic
Advanced ceramics advanced ceramics chemical bonding.
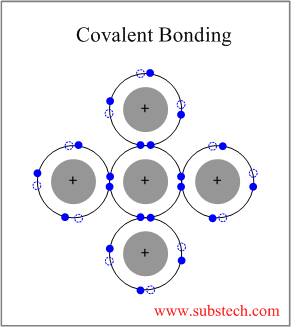
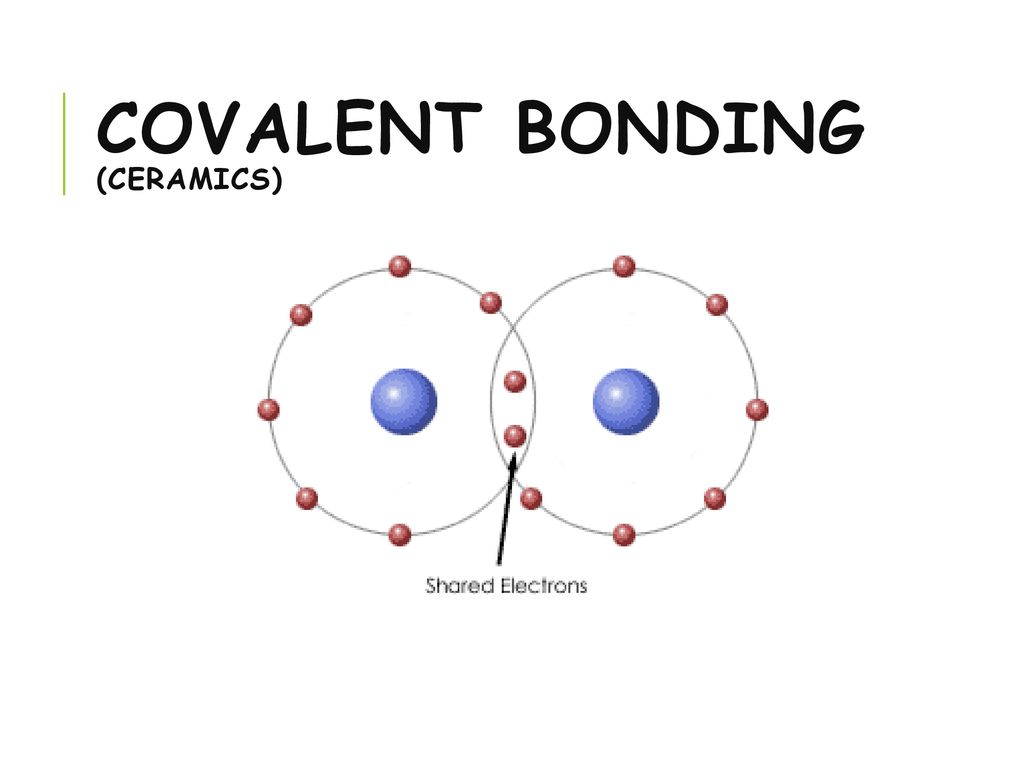
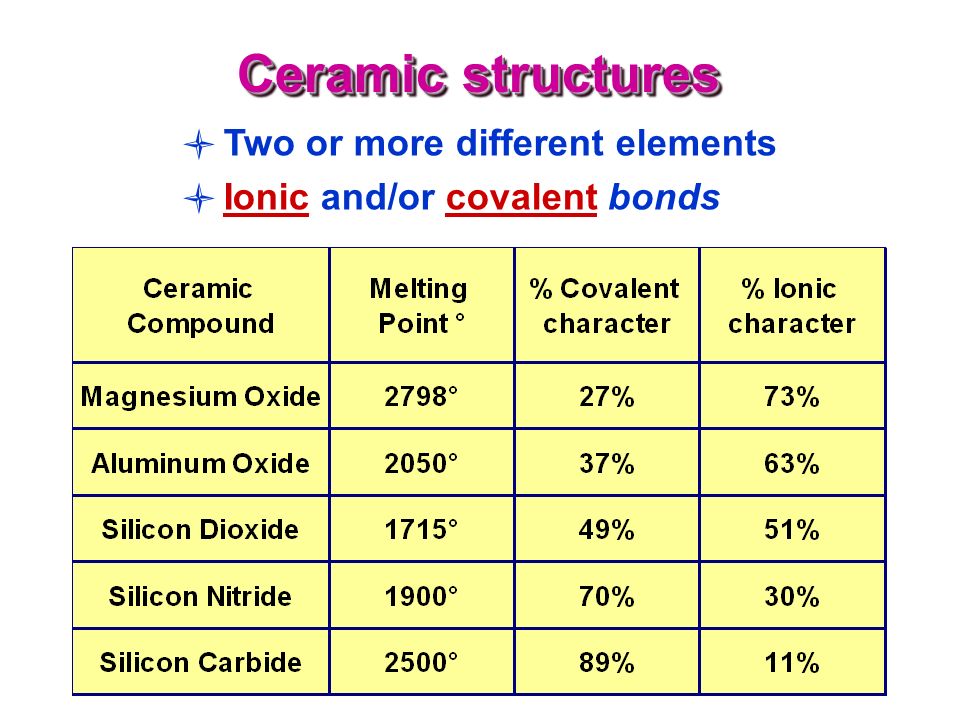
Covalent bond ceramic. A material held together by either type of bond will tend to fracture before any plastic deformation takes place which results in poor toughness in these materials. Underlying many of the properties found in ceramics are the strong primary bonds that hold the atoms together and form the ceramic material. What determines whether a covalent bond forms. The atoms in these ceramics are arranged so that each pair of nearest neighbour atoms forms a chemical bond by sharing a pair of electrons.
Having started as a hobby today we lead the innovation in ceramic coating nanotechnology. When two dissimilar nonmetals form bonds e g hydrogen and oxygen they will form a covalent bond but the electrons will spend more time. So if two identical nonmetals e g two hydrogen atoms bond together they will form a pure covalent bond. The bonding of atoms together is much stronger in covalent and ionic bonding than in metallic.
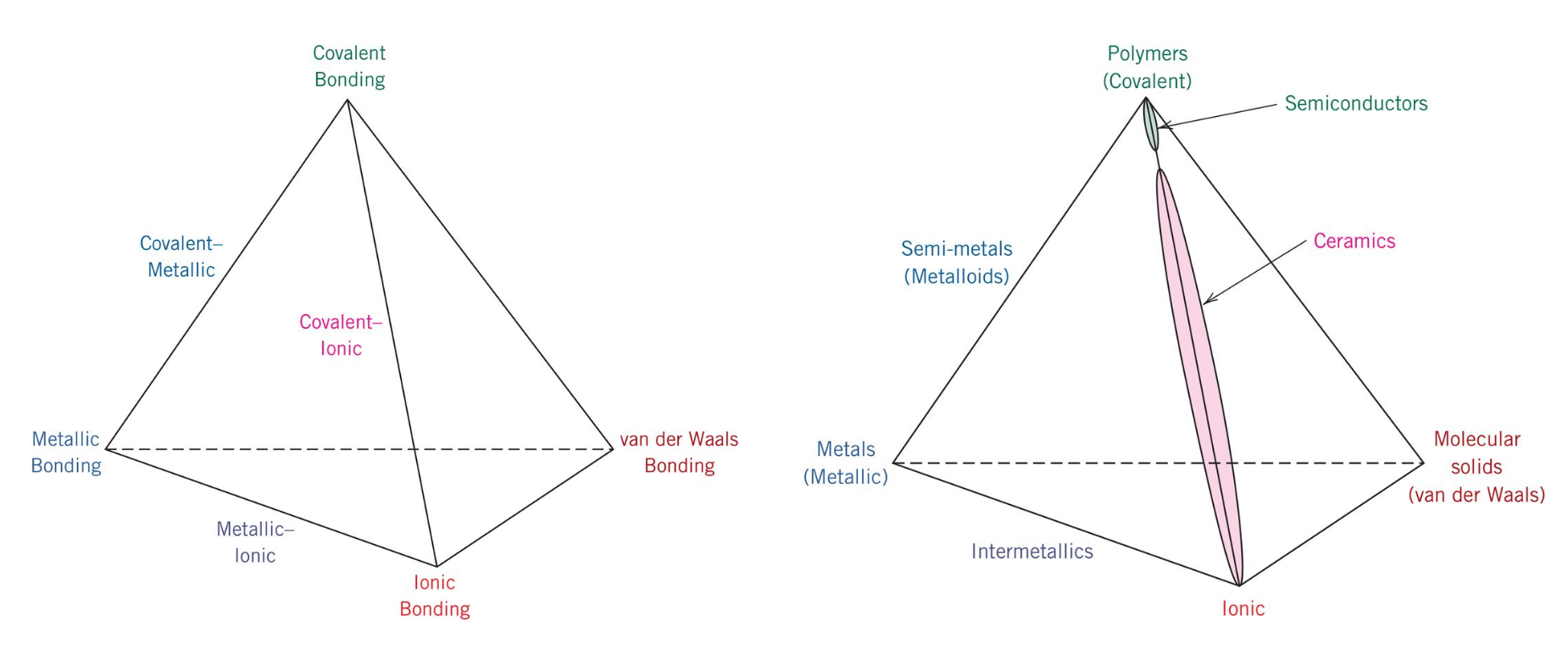
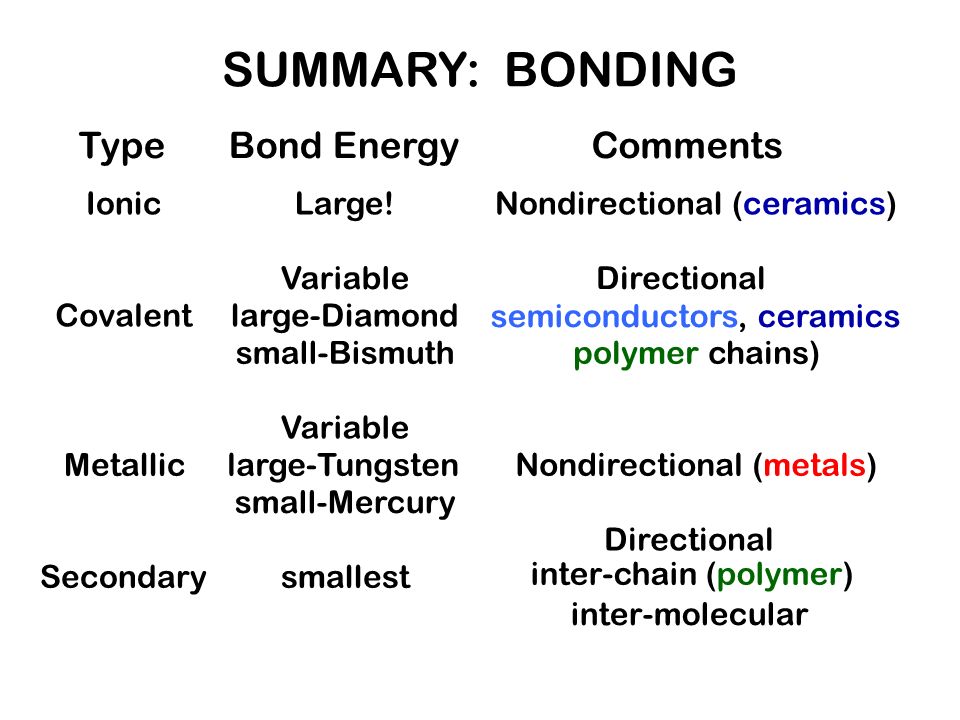
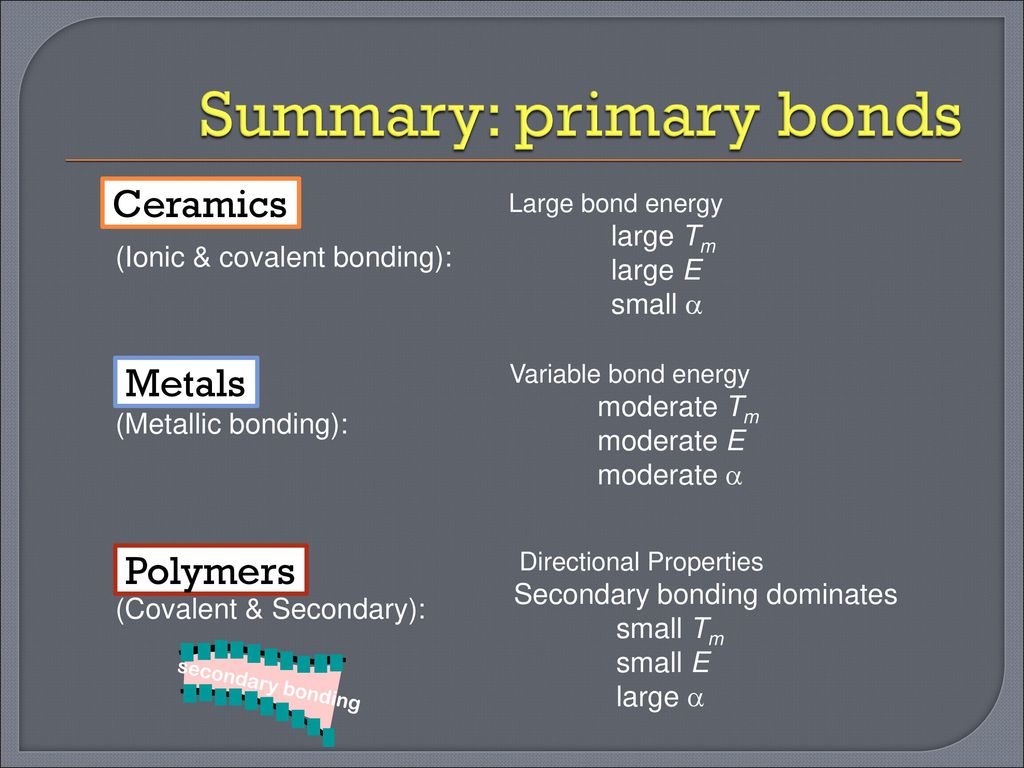
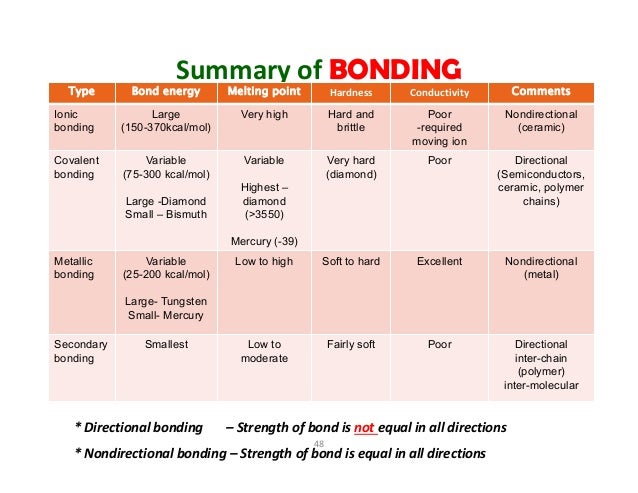
In ionic bonding a metal atom donates electrons and a nonmetal atom accepts electrons. These chemical bonds are of two types. Covalent bonding is found in many ceramic structures such as sic bn and diamond. For metals the chemical bond is called the metallic bond.
The atoms in ceramic materials are held together by a chemical bond. Reaction bonded silicon nitride rbsn is made from finely divided silicon powders that are formed to shape and subsequently reacted in a mixed nitrogen hydrogen or nitrogen helium atmosphere at 1 200 to 1 250 c 2 200 to 2 300 f. Reaction sintering or reaction bonding is an important means of producing dense covalent ceramics. Compounds with covalent bonds may be solid liquid or gas at room temperature depending on the number of atoms in the compound.
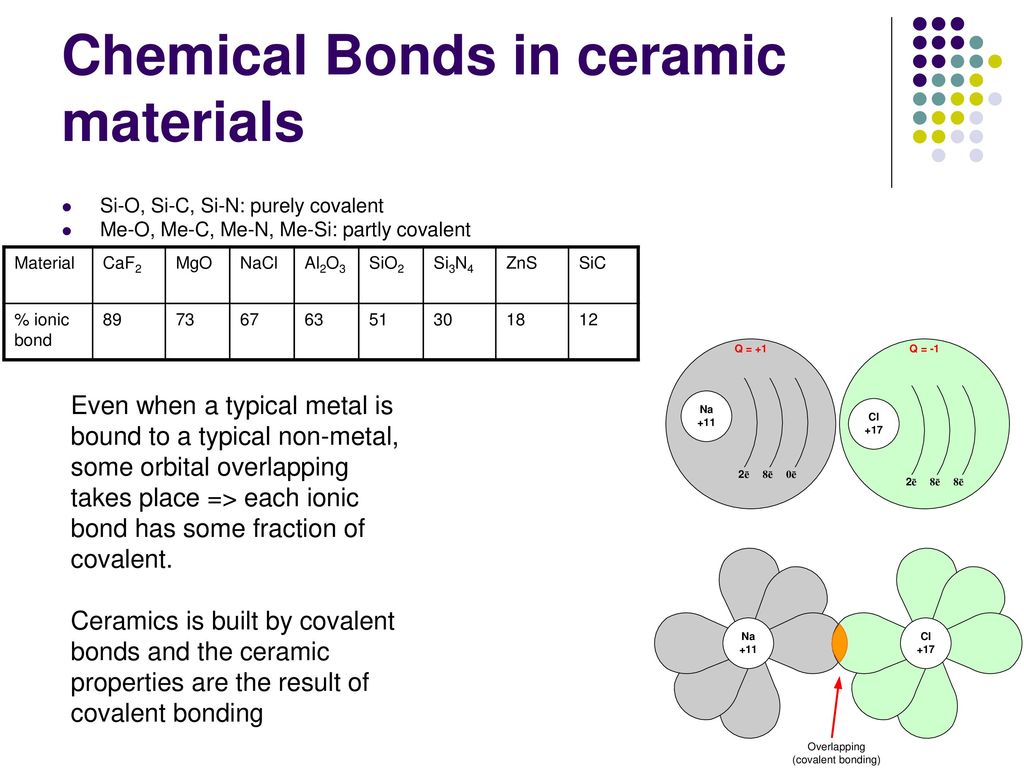
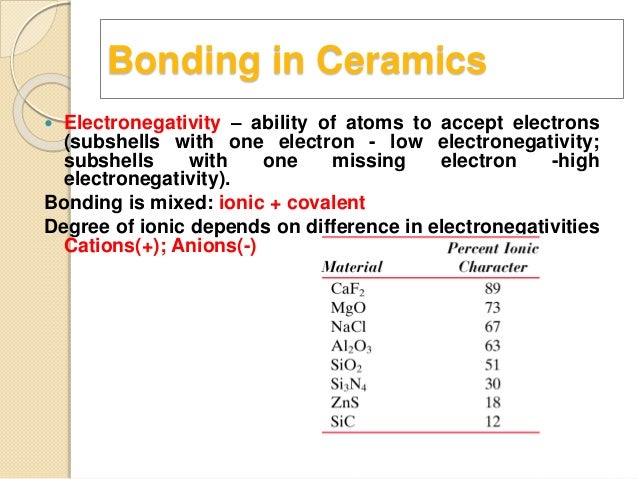
Kovalent coatings journey has been one involving great dedication for quality. The two most common chemical bonds for ceramic materials are covalent and ionic. The high energy of covalent bonds makes these ceramics very stable with regard to chemical and thermal. Covalent bonding instead occurs between two nonmetals in other words two atoms that have similar electronegativity and involves the sharing of electron pairs between the two atoms.
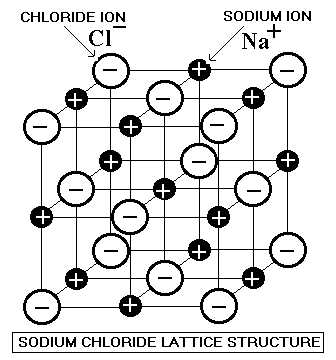
The more atoms in each molecule the higher a compound s melting and boiling temperature will be. Kovalent coatings the pinnacle in ceramic coating nanotechnology. This electron transfer creates positive metal ions cations and negative nonmetal ions anions which are attracted to each other through coulombic attraction. Ceramic materials are usually ionic or covalent bonded materials and can be crystalline or amorphous.
Covalent bonds form when two nonmetallic atoms have the same or similar electronegativity values. Our r d team has developed breakthrough formulas that have set a standard for the ceramic coating industry. Recall that the predominant bonding for ceramic materials is ionic bonding. Since most covalent compounds contain only a few atoms and the forces.